mybatis-spring-boot-starter可以帮助你快速创建基于Spring Boot的MyBatis应用程序。
● 构建独立的MyBatis应用程序
● 零模板
● 更少的XML配置文件
引入mybatis-spring-boot-starter模块之后,其可以:
● 自动检测DataSource
● 使用SqlSessionFactoryBean注册SqlSessionFactory 实例,并设置DataSource数据源
● 基于SqlSessionFactory自动注册SqlSessionTemplate实例
● 自动扫描@Mapper注解类,并通过SqlSessionTemplate注册到Spring Context中
mybatis-spring-boot-starter就是参照Spring Boot的设计思想,化繁为简,以简单注解的方式让用户快速上手。
下面我们简单的创建一个项目,让他跑起来:
首先,我们引入依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.1.0</version> </dependency>配置数据源
spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/auto?useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&characterEncoding=utf8 username: root password: root driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver创建Mapper
@Repository public interface UserMapper { @Select("SELECT * FROM Person WHERE id = #{id}") Person selectUser(int id); @Delete("delete from person where id = #{id}") void deleteByPrimaryKey(int id); }启动类:
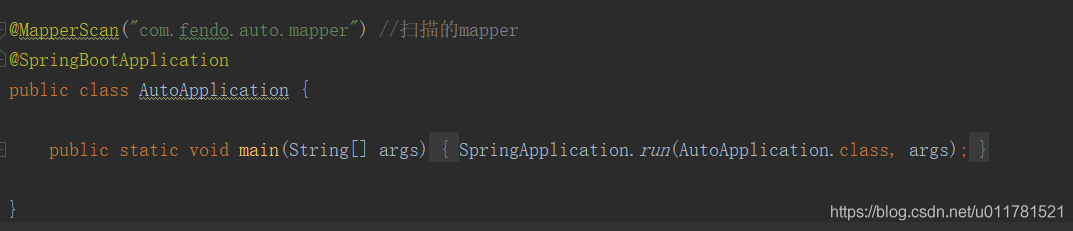
@MapperScan("com.fendo.auto.mapper") //扫描的mapper @SpringBootApplication public class AutoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(AutoApplication.class, args); } }这样就完成了一个简单的集成
mybatis-spring-boot-starter的作用就是,在SpringBoot启动时,去扫描所有Mapper接口,然后为其增加一个代理实现类,在调用的过程中,我们实际调用的是这个代理对象。用过springboot的同学都是知道,springboot配置简单,更提供了大量的starter方便集成各个组件。每个组件基本只要依赖了jar包,基本不需要或者需要少量的配置信息就可以直接使用了,那么在这简单的starter背后的原理是什么呢?
统一的命名规范 XXX-spring-boot-starter (非必须)
你如果去看每个starter的的名字,比如mybatis的starter名字如下:
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.1.0</version> </dependency>你会发现每个starter的artifactId都是以spring-boot-starter结尾,这个是普遍认同的一个规范,不是必须按照这个名字来,也可以自定义名字,原因下面介绍。
统一的配置文件 spring.factories
必须在classpath下的META-INF文件夹下创建一个spring.factories,本质是一个Properties,所以得按照key-value的形式进行配置。自动配置的key是org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration。我们看下mybatis的配置:
# Auto Configure org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ org.mybatis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.MybatisLanguageDriverAutoConfiguration,\ org.mybatis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.MybatisAutoConfiguration我们看到,这个文件配置了一个key:value格式的数据
1)key是:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration
2)value是:org.mybatis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.MybatisLanguageDriverAutoConfiguration,org.mybatis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.MybatisAutoConfiguration
key声明的是一个接口,value则是这个接口对应的实现类,如果有多个则以","符号分割。
简单来说,spring.factories就像是工厂一样配置了大量的接口对应的实现类,我们通过这些配置 + 反射处理就可以拿到相应的实现类。这种类似于插件式的设计方式,只要引入对应的jar包,那么对应的spring.factories就会被扫描到,对应的实现类也就会被实例化,如果不需要的时候,直接把jar包移除即可。
注解说明:
@Configuration Configuration 是springboot提供的,表示这是一个配置类,其实它的作用跟@Bean是一样的,都是让spring实例化该类。 @ConditionalOnClass 表示存在某些类的时候,才进行初始化。 @AutoConfigureBefore 表示必须先初始化某个类 @AutoConfigureAfter 表示初始化完成之后加载某个类 @ConditionalOnBean 只有在上下文中存在某个类才运行 @EnableConfigurationProperties ConfigurationProperties注解主要用来把properties配置文件转化为bean来使用的 而@EnableConfigurationProperties注解的作用是@ConfigurationProperties注解生效。 如果只配置@ConfigurationProperties注解,在IOC容器中是获取不到properties配置文件转化的bean的。 @ConditionalOnMissingBean 作用在@bean定义上,它的作用就是在容器加载它作用的bean时 检查容器中是否存在目标类型(ConditionalOnMissingBean注解的value值)的bean了 如果存在这跳过原始bean的BeanDefinition加载动作。 简单理解就是@ConditionalOnBean是依赖,@ConditionalOnMissBean是排斥,@Conditional为条件 @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate 当给定类型的bean存在并且指定为Primary的给定类型存在时,返回true @ConditionalOnMissingBean 当给定的类型、类名、注解、昵称在beanFactory中不存在时返回true.各类型间是or的关系 @ConditionalOnBean 与上面相反,要求bean存在 @ConditionalOnMissingClass 当给定的类名在类路径上不存在时返回true,各类型间是and的关系 @ConditionalOnClass 与上面相反,要求类存在 @ConditionalOnCloudPlatform 当所配置的CloudPlatform为激活时返回true @ConditionalOnExpression spel表达式执行为true @ConditionalOnJava 运行时的java版本号是否包含给定的版本号.如果包含,返回匹配,否则,返回不匹配 @ConditionalOnProperty 要求配置属性匹配条件 @ConditionalOnJndi 给定的jndi的Location 必须存在一个.否则,返回不匹配 @ConditionalOnNotWebApplication web环境不存在时 @ConditionalOnWebApplication web环境存在时 @ConditionalOnResource 要求制定的资源存在mybatis-spring-boot-starter中最主要的一个类就是MybatisAutoConfiguration,MybatisAutoConfiguration 是spring boot 下 mybatis 默认的配置类,只要开启了注释了 @EnableAutoConfiguration 就可以了,spring boot 会默认执行。在SpringBoot启动的过程中 @SpringBootApplication 中组合了 EnableAutoConfiguration ,属于spring boot 自动配置和启动过程,SpringBoot启动时会进入到MybatisAutoConfiguration这个类里,这是一个自动配置类,这里面初始化了SqlSessionFactory、SqlSessionTemplate等一些我们在Spring项目中需要手动配置的,源码如下该类如下:
//Configuration注解:说明这是spring的配置项,容器初始化的时候要进行解析处理 @org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration //ConditionalOnClass注解:有类SqlSessionFactory(Mybatis),SqlSessionFactoryBean(Mybatis-Spring)的时候才进行解析处理 @ConditionalOnClass({SqlSessionFactory.class, SqlSessionFactoryBean.class}) //ConditionalOnBean注解:容器中有DataSource Bean的时候才进行解析处理 @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(DataSource.class) //ConfigurationProperties注解主要用来把properties配置文件转化为bean来使用的 //而EnableConfigurationProperties注解的作用是ConfigurationProperties注解生效。 //如果只配置@ConfigurationProperties注解,在IOC容器中是获取不到properties配置文件转化的bean的。 //MybatisProperties是mybatis的配置类,将properties中的配置文件转换成MybatisProperties对象 //MybatisProperties上有@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mybatis")注解。 //EnableConfigurationProperties注解和MybatisProperties类:配置自己的Mybatis 属性,在Application.Properties中。 @EnableConfigurationProperties(MybatisProperties.class) //AutoConfigureAfter注解: 在DataSourceAutoConfiguration,MybatisLanguageDriverAutoConfiguration后解析 @AutoConfigureAfter({DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class, MybatisLanguageDriverAutoConfiguration.class}) public class MybatisAutoConfiguration implements InitializingBean { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MybatisAutoConfiguration.class); private final MybatisProperties properties; private final Interceptor[] interceptors; private final TypeHandler[] typeHandlers; private final LanguageDriver[] languageDrivers; private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader; private final DatabaseIdProvider databaseIdProvider; private final List<ConfigurationCustomizer> configurationCustomizers; /** * 构造方法 * @param properties * @param interceptorsProvider * @param typeHandlersProvider * @param languageDriversProvider * @param resourceLoader * @param databaseIdProvider * @param configurationCustomizersProvider */ public MybatisAutoConfiguration(MybatisProperties properties, ObjectProvider<Interceptor[]> interceptorsProvider, ObjectProvider<TypeHandler[]> typeHandlersProvider, ObjectProvider<LanguageDriver[]> languageDriversProvider, ResourceLoader resourceLoader, ObjectProvider<DatabaseIdProvider> databaseIdProvider, ObjectProvider<List<ConfigurationCustomizer>> configurationCustomizersProvider) { this.properties = properties; this.interceptors = interceptorsProvider.getIfAvailable(); this.typeHandlers = typeHandlersProvider.getIfAvailable(); this.languageDrivers = languageDriversProvider.getIfAvailable(); this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader; this.databaseIdProvider = databaseIdProvider.getIfAvailable(); this.configurationCustomizers = configurationCustomizersProvider.getIfAvailable(); } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { checkConfigFileExists(); } private void checkConfigFileExists() { if (this.properties.isCheckConfigLocation() && StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) { Resource resource = this.resourceLoader.getResource(this.properties.getConfigLocation()); Assert.state(resource.exists(), "Cannot find config location: " + resource + " (please add config file or check your Mybatis configuration)"); } } /** * 创建SqlSessionFactory * @param dataSource * @return * @throws Exception */ @Bean //@ConditionalOnMissingBean注解判断是否执行初始化代码,即如果用户已经创建了bean,则相关的初始化代码不再执行。 @ConditionalOnMissingBean public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception { SqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); factory.setDataSource(dataSource); factory.setVfs(SpringBootVFS.class); if (StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) { factory.setConfigLocation(this.resourceLoader.getResource(this.properties.getConfigLocation())); } //应用配置 applyConfiguration(factory); if (this.properties.getConfigurationProperties() != null) { factory.setConfigurationProperties(this.properties.getConfigurationProperties()); } if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.interceptors)) { factory.setPlugins(this.interceptors); } if (this.databaseIdProvider != null) { factory.setDatabaseIdProvider(this.databaseIdProvider); } if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeAliasesPackage())) { factory.setTypeAliasesPackage(this.properties.getTypeAliasesPackage()); } if (this.properties.getTypeAliasesSuperType() != null) { factory.setTypeAliasesSuperType(this.properties.getTypeAliasesSuperType()); } if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeHandlersPackage())) { factory.setTypeHandlersPackage(this.properties.getTypeHandlersPackage()); } if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.typeHandlers)) { factory.setTypeHandlers(this.typeHandlers); } if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.properties.resolveMapperLocations())) { factory.setMapperLocations(this.properties.resolveMapperLocations()); } Set<String> factoryPropertyNames = Stream .of(new BeanWrapperImpl(SqlSessionFactoryBean.class).getPropertyDescriptors()).map(PropertyDescriptor::getName) .collect(Collectors.toSet()); Class<? extends LanguageDriver> defaultLanguageDriver = this.properties.getDefaultScriptingLanguageDriver(); if (factoryPropertyNames.contains("scriptingLanguageDrivers") && !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.languageDrivers)) { // Need to mybatis-spring 2.0.2+ factory.setScriptingLanguageDrivers(this.languageDrivers); if (defaultLanguageDriver == null && this.languageDrivers.length == 1) { defaultLanguageDriver = this.languageDrivers[0].getClass(); } } if (factoryPropertyNames.contains("defaultScriptingLanguageDriver")) { // Need to mybatis-spring 2.0.2+ factory.setDefaultScriptingLanguageDriver(defaultLanguageDriver); } return factory.getObject(); } /** * 应用配置 * @param factory */ private void applyConfiguration(SqlSessionFactoryBean factory) { Configuration configuration = this.properties.getConfiguration(); if (configuration == null && !StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) { configuration = new Configuration(); } if (configuration != null && !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.configurationCustomizers)) { //ConfigurationCustomizer 属于 mybatis-spring包中的接口 //ConfigurationCustomizer 主要是提供一个接口可以获取 mybatis 的 configuration 或者更改 configuration 中的属性,比如向configuration 中注册插件 for (ConfigurationCustomizer customizer : this.configurationCustomizers) { customizer.customize(configuration); } } factory.setConfiguration(configuration); } /** * 创建sqlSessionTemplate * @param sqlSessionFactory * @return */ @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) { ExecutorType executorType = this.properties.getExecutorType(); if (executorType != null) { return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory, executorType); } else { return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory); } } /** * This will just scan the same base package as Spring Boot does. If you want more power, you can explicitly use * {@link org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan} but this will get typed mappers working correctly, out-of-the-box, * similar to using Spring Data JPA repositories. */ public static class AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar implements BeanFactoryAware, ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { private BeanFactory beanFactory; @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { if (!AutoConfigurationPackages.has(this.beanFactory)) { logger.debug("Could not determine auto-configuration package, automatic mapper scanning disabled."); return; } logger.debug("Searching for mappers annotated with @Mapper"); List<String> packages = AutoConfigurationPackages.get(this.beanFactory); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { packages.forEach(pkg -> logger.debug("Using auto-configuration base package '{}'", pkg)); } //处理@Mapper标记的接口 BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(MapperScannerConfigurer.class); builder.addPropertyValue("processPropertyPlaceHolders", true); builder.addPropertyValue("annotationClass", Mapper.class); builder.addPropertyValue("basePackage", StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(packages)); BeanWrapper beanWrapper = new BeanWrapperImpl(MapperScannerConfigurer.class); Stream.of(beanWrapper.getPropertyDescriptors()) // Need to mybatis-spring 2.0.2+ .filter(x -> x.getName().equals("lazyInitialization")).findAny() .ifPresent(x -> builder.addPropertyValue("lazyInitialization", "${mybatis.lazy-initialization:false}")); registry.registerBeanDefinition(MapperScannerConfigurer.class.getName(), builder.getBeanDefinition()); } @Override public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } } /** * If mapper registering configuration or mapper scanning configuration not present, this configuration allow to scan * mappers based on the same component-scanning path as Spring Boot itself. */ @org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration //把用到的资源导入到当前容器中 //@Import注解把AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar的bean注入到当前容器中。 @Import(AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar.class) //如果在容器中没有 MapperFactoryBean ,MapperScannerConfigurer就导入AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar 配置类。 @ConditionalOnMissingBean({MapperFactoryBean.class, MapperScannerConfigurer.class}) public static class MapperScannerRegistrarNotFoundConfiguration implements InitializingBean { @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { logger.debug( "Not found configuration for registering mapper bean using @MapperScan, MapperFactoryBean and MapperScannerConfigurer."); } } }所用的注解就是上面所说的:
Configuration注解:说明这是spring的配置项,容器初始化的时候要进行解析处理 ConditionalOnClass注解:有类SqlSessionFactory(Mybatis),SqlSessionFactoryBean(Mybatis-Spring)的时候才进行解析处理 ConditionalOnBean:容器中有DataSource Bean的时候才进行解析处理 AutoConfigureAfter注解: 在DataSourceAutoConfiguration后解析 EnableConfigurationProperties注解和MybatisProperties类:配置自己的Mybatis 属性,在Application.Properties中。其中有个MapperScannerRegistrarNotFoundConfiguration静态方法:
@org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration //把用到的资源导入到当前容器中 //@Import注解把AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar的bean注入到当前容器中。 @Import(AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar.class) //如果在容器中没有 MapperFactoryBean ,MapperScannerConfigurer就导入AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar 配置类。 @ConditionalOnMissingBean({MapperFactoryBean.class, MapperScannerConfigurer.class}) public static class MapperScannerRegistrarNotFoundConfiguration implements InitializingBean { @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { logger.debug( "Not found configuration for registering mapper bean using @MapperScan, MapperFactoryBean and MapperScannerConfigurer."); } }这个类实现了Spring的注册bean的接口,并注册了一个MapperScannerConfigurer,如果在启动类上面没有@MapperScan就会执行AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar查找扫描出标注有 @Mapper 注解类的接口,并注册到Spring容器中。
@Mapper与@MapperScan
在项目中大多数用的都是@MapperScan注解,指定basePackages,扫描mybatis Mapper接口类
另外一种方式是用@Mapper注解,其实这两种方法扫描配置用的是一个地方,只是扫描入口不同。从mybatis3.4.0开始加入了@Mapper注解,目的就是为了不再写mapper映射文件(xxxxMapper.xml),用法也很简单:
** * 添加了@Mapper注解之后这个接口在编译时会生成相应的实现类 * * 需要注意的是:这个接口中不可以定义同名的方法,因为会生成相同的id * 也就是说这个接口是不支持重载的 */ @Mapper public interface User { @Select("select * from user where name = #{name}") public User find(String name); @Select("select * from user where name = #{name} and pwd = #{pwd}") /** * 对于多个参数来说,每个参数之前都要加上@Param注解, * 要不然会找不到对应的参数进而报错 */ public User login(@Param("name")String name, @Param("pwd")String pwd); }这种方式需要每个接口上面都加上这个注解,很麻烦,所以就出现了@MapperScan,@MapperScan只需要指定包名就行了,会自动扫描。
@MapperScan是根据其注解上MapperScannerRegistrar进行自动配置的,最终调用的自动配置代码和下面的代码一致,@Mapper自动配置的程序入口是 MybatisAutoConfiguration类的最下面,位置在mybatis-spring-boot-starter包下面的mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure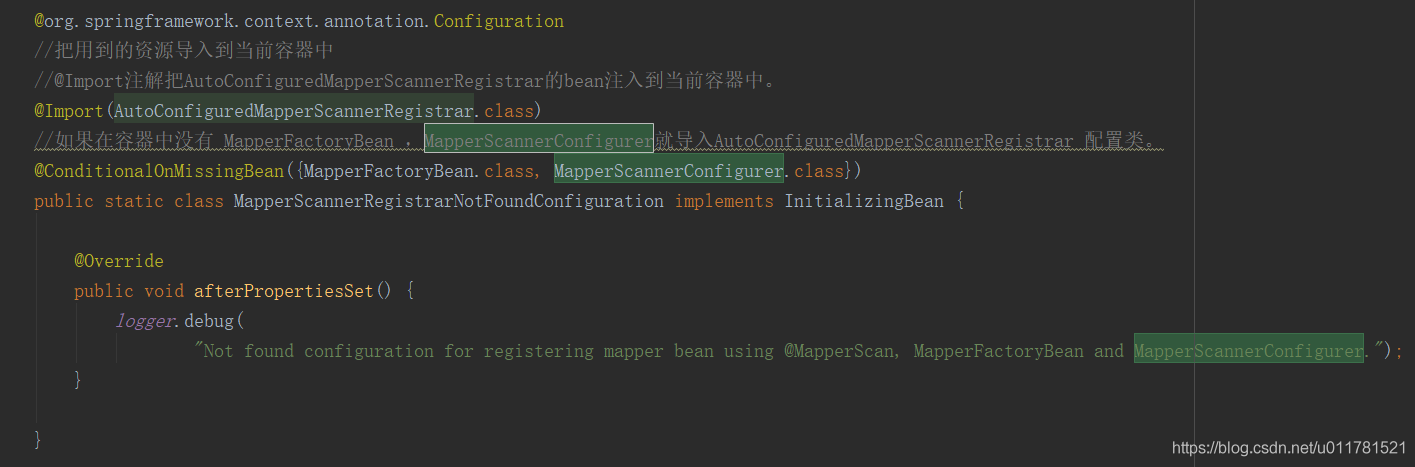
上面代码的逻辑是 如果标注了@MapperScan 的注解,将会生成 MapperFactoryBean, 如果没有标注@MapperScan 也就是没有MapperFactoryBean的实例,就走@Import里面的配置,下面看看AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar的配置,它是MybatisAutoConfiguration类下的内部类,MapperScannerConfigurer类实现了spring的注册bean的接口,最主要的方法就是postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry
@Override public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders) { processPropertyPlaceHolders(); } ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry); scanner.setAddToConfig(this.addToConfig); scanner.setAnnotationClass(this.annotationClass); scanner.setMarkerInterface(this.markerInterface); scanner.setSqlSessionFactory(this.sqlSessionFactory); scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate); scanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName); scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName); scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext); scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(this.nameGenerator); scanner.setMapperFactoryBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass); if (StringUtils.hasText(lazyInitialization)) { scanner.setLazyInitialization(Boolean.valueOf(lazyInitialization)); } scanner.registerFilters(); scanner.scan( StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS)); }这个方法中实例化了一个ClassPathMapperScanner,并调用了scan方法,点击进去之后
@Override public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) { Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages); if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) { LOGGER.warn(() -> "No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages) + "' package. Please check your configuration."); } else { processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions); } return beanDefinitions; } private void processBeanDefinitions(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions) { GenericBeanDefinition definition; for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) { definition = (GenericBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition(); String beanClassName = definition.getBeanClassName(); LOGGER.debug(() -> "Creating MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "' and '" + beanClassName + "' mapperInterface"); // the mapper interface is the original class of the bean // but, the actual class of the bean is MapperFactoryBean definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(beanClassName); // issue #59 definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass); definition.getPropertyValues().add("addToConfig", this.addToConfig); boolean explicitFactoryUsed = false; if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)) { definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)); explicitFactoryUsed = true; } else if (this.sqlSessionFactory != null) { definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", this.sqlSessionFactory); explicitFactoryUsed = true; } if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)) { if (explicitFactoryUsed) { LOGGER.warn( () -> "Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored."); } definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)); explicitFactoryUsed = true; } else if (this.sqlSessionTemplate != null) { if (explicitFactoryUsed) { LOGGER.warn( () -> "Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored."); } definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", this.sqlSessionTemplate); explicitFactoryUsed = true; } if (!explicitFactoryUsed) { LOGGER.debug(() -> "Enabling autowire by type for MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "'."); definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE); } definition.setLazyInit(lazyInitialization); } }这个就是spring boot注册mapper的核心方法了,在上面的方法中可以发现通过definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass)为我们定义的mapper添加了一个代理对象MapperFactoryBean,前往MapperFactoryBean可以发现这个类实现了Spring提供的FactoryBean接口,里面有个核心方法
public T getObject() throws Exception { return this.getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface); }这个方法是放回一个bean对象,继续进入getMapper()方法
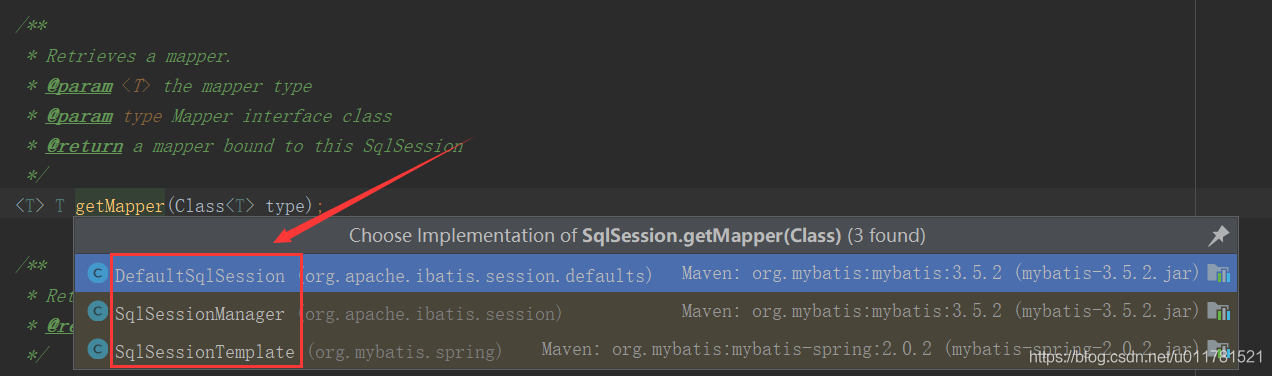
该方法有三个实现类,选择DefaultSqlSession
@Override public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) { return configuration.getMapper(type, this); }调用的是Configuration中的
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession); }找到MapperRegister类,里面有一个核心方法
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory)this.knownMappers.get(type); if (mapperProxyFactory == null) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry."); } else { try { return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); } catch (Exception var5) { throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + var5, var5); } } }这个方法通过调用MapperProxyFactory类,生成一个代理实例MapperProxy并返回,MapperProxyFactory类源码如下
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> { private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) { this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; } public Class<T> getMapperInterface() { return mapperInterface; } public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() { return methodCache; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) { return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy); } public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache); return newInstance(mapperProxy); } }到这里,SpringBoot初始化Mapper完毕,接下来在我们调用自己定义的Mapper的时候,实际上调用的便是MapperProxy这个代理对象了,MapperProxy类实现了InvocationHandler接口,这个类中最核心的方法便是Invoke方法
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L; private final SqlSession sqlSession; private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache; public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) { this.sqlSession = sqlSession; this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; this.methodCache = methodCache; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { return method.invoke(this, args); } else if (method.isDefault()) { return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args); } } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method); return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args); } private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) { return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method, k -> new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration())); } private Object invokeDefaultMethod(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { final Constructor<MethodHandles.Lookup> constructor = MethodHandles.Lookup.class .getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, int.class); if (!constructor.isAccessible()) { constructor.setAccessible(true); } final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass(); return constructor .newInstance(declaringClass, MethodHandles.Lookup.PRIVATE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PROTECTED | MethodHandles.Lookup.PACKAGE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PUBLIC) .unreflectSpecial(method, declaringClass).bindTo(proxy).invokeWithArguments(args); } }通过mapperMethod.execute()方法去执行mybatis自己封装的操作数据库的操作了,execute()源码如下:
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { Object result; switch (command.getType()) { case INSERT: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param)); break; } case UPDATE: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param)); break; } case DELETE: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param)); break; } case SELECT: if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) { executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args); result = null; } else if (method.returnsMany()) { result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args); } else if (method.returnsMap()) { result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args); } else if (method.returnsCursor()) { result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args); } else { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param); if (method.returnsOptional() && (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) { result = Optional.ofNullable(result); } } break; case FLUSH: result = sqlSession.flushStatements(); break; default: throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName()); } if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) { throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ")."); } return result; }热门文章
- 3月27日 | HiddifyNextNode机场节点订阅每天更新22.8M/S免费节点订阅链接
- 4月5日 | HiddifyNextNode机场节点订阅每天更新18.6M/S免费节点订阅链接
- 同城领养狗狗 同城领养狗狗的一般在什么平台
- js+jQuery实现网页打字机效果(带光标)
- 国内宠物粮生产厂家有哪些 国内宠物粮生产厂家有哪些品牌
- 3月7日 | HiddifyNextNode机场节点订阅每天更新18.4M/S免费节点订阅链接
- pgpool-II 4.3中文手册入门教程
- mybatis-spring-boot-starter 原理分析
- 上海宠物领养中心官网电话(上海宠物领养中心官网电话号码)
- 浆液循环泵厂家(中国循环水泵十大名牌)